*Equal contribution

We introduce -Sampler, an SMC-based framework incorporating pCNL-based initial particle sampling for effective inference-time reward alignment with a score-based generative model. Inference-time reward alignment with score-based generative models has recently gained significant traction, following a broader paradigm shift from pre-training to post-training optimization. At the core of this trend is the application of Sequential Monte Carlo (SMC) to the denoising process. However, existing methods typically initialize particles from the Gaussian prior, which inadequately captures reward-relevant regions and results in reduced sampling efficiency. We demonstrate that initializing from the reward-aware posterior significantly improves alignment performance. To enable posterior sampling in high-dimensional latent spaces, we introduce the preconditioned Crank–Nicolson Langevin (pCNL) algorithm, which combines dimension-robust proposals with gradient-informed dynamics. This approach enables efficient and scalable posterior sampling and consistently improves performance across various reward alignment tasks, including layout-to-image generation, quantity-aware generation, and aesthetic-preference generation, as demonstrated in our experiments.
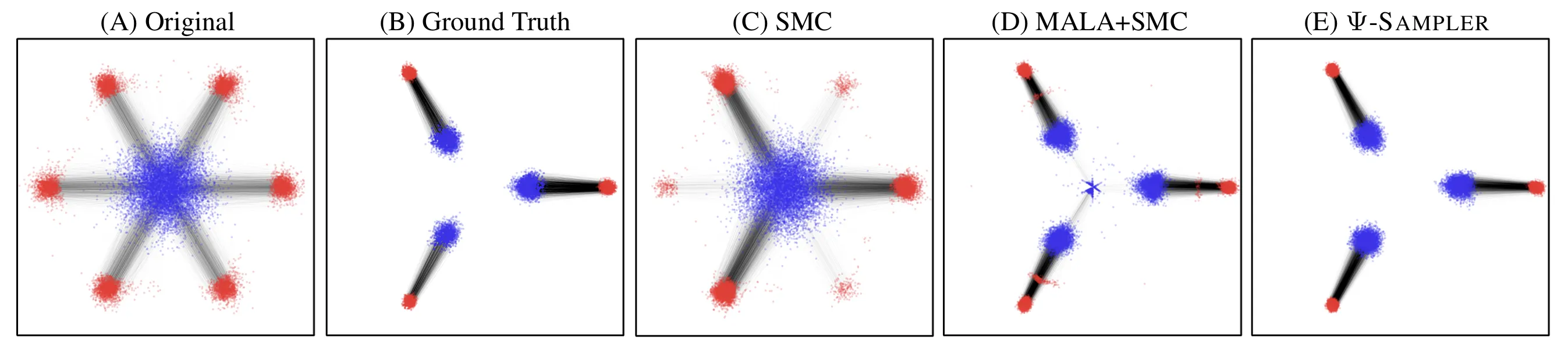
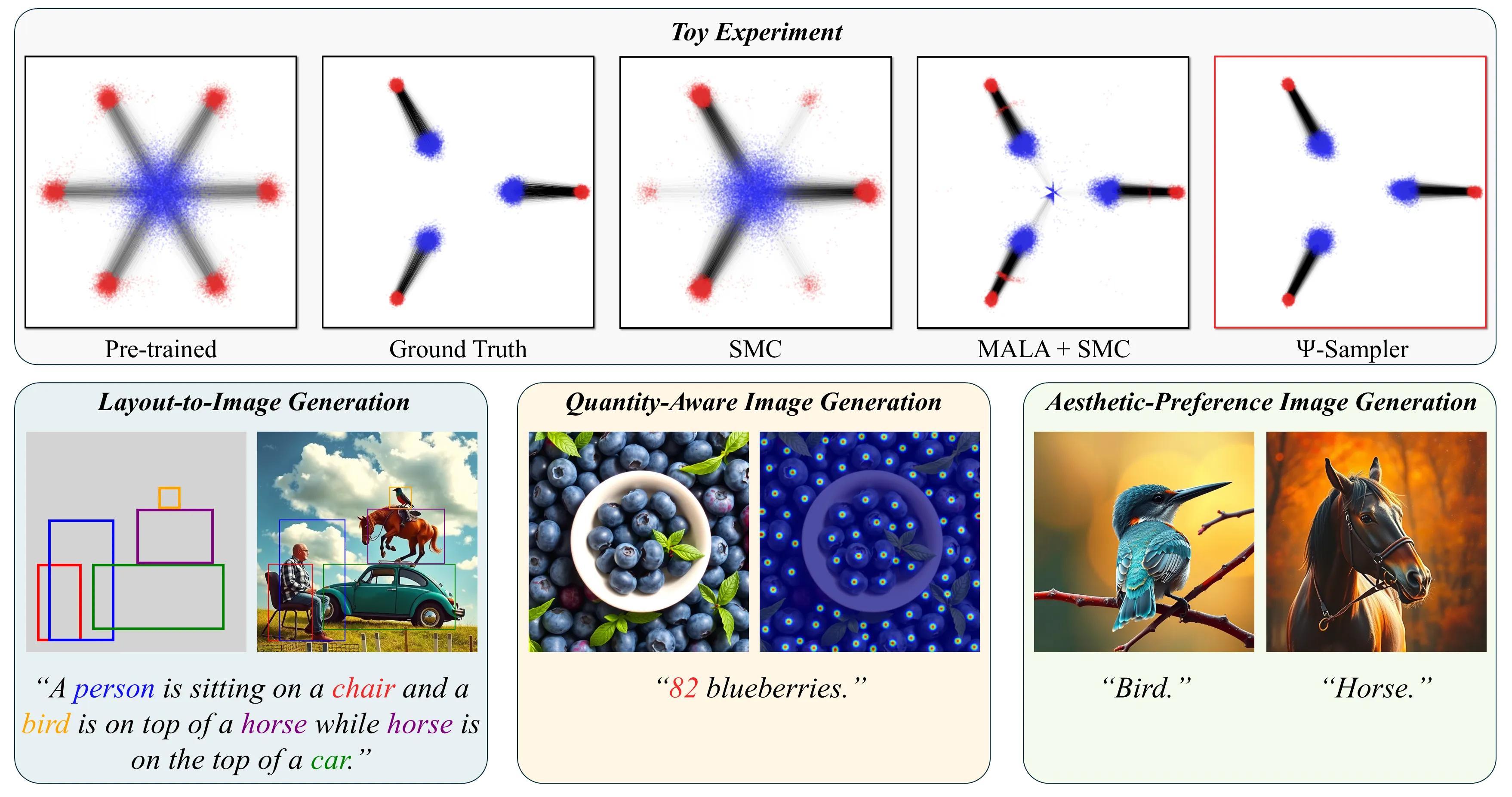
We visualize how different initialization strategies affect the performance of Sequential Monte Carlo (SMC) in a synthetic 2D task.
(A) shows raw samples from the prior distribution (blue), and the generation results from the pre-trained score-based generative model without reward guidance (red).
(B) shows the target distribution (red) defined by a reward that selects specific modes, and the posterior distribution (blue).
Each panel (C)-(E) overlays:
🔴 Red dots: clean data samples obtained through SMC with inference-time reward alignment, where the proposal kernel is based on the denoising process of pre-trained score-based generative model.
🔵 Blue dots: initial samples used to start SMC sampling.
While standard SMC (C) fails to cover all modes, and Metropolis-Adjusted Langevin Algorithm (MALA) + SMC (D) still leaves some gaps, our proposed -Sampler (E) achieves the closest match to the target. This highlights the importance of high-quality initial particles in reward-guided inference.
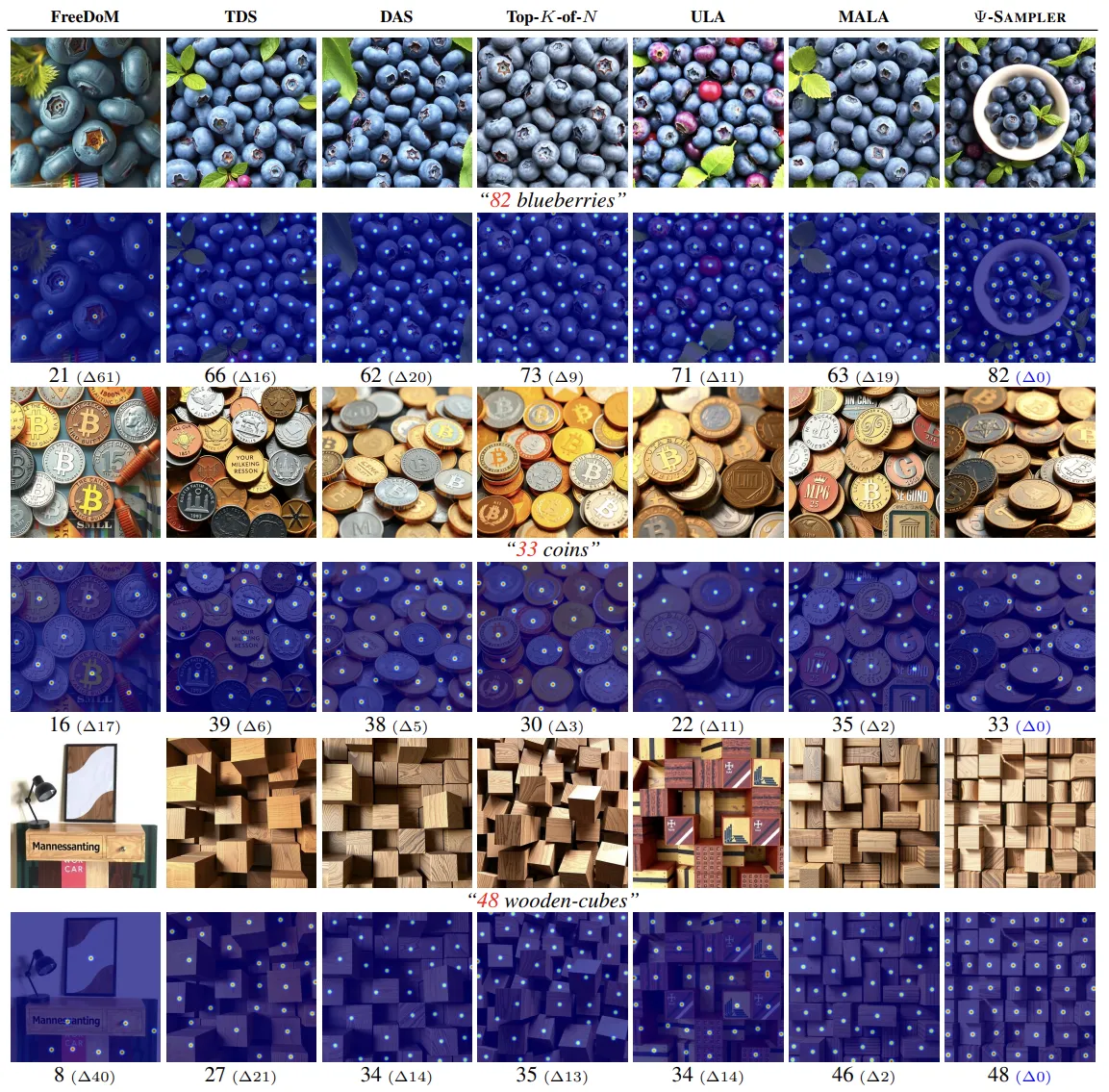
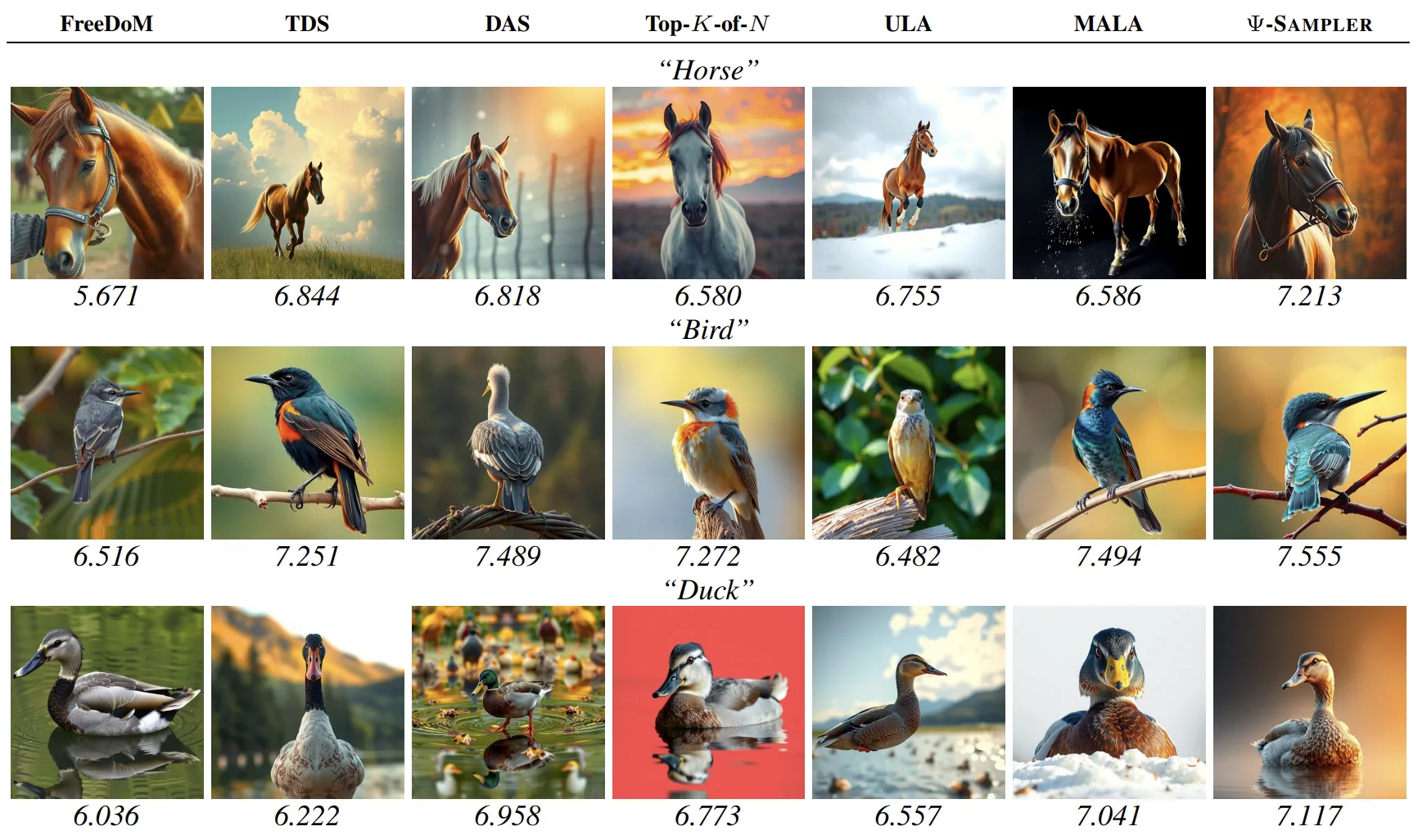
We provide qualitative results comparing various baselines with our -Sampler. We conducted experiments on three applications: Layout-to-Image Generation, Quantity-Aware Image Generation, and Aesthetic-Preference Image Generation.
Single-Particle: FreeDoM [1] is a non-SMC method that relies on a single particle.
SMC Initialized with Prior Distribution Samples: TDS [2] serves as the SMC baseline, while DAS [3] extends it with a tempering strategy.
SMC Initialized with Posterior Distribution Samples: We compare four posterior-based initialization strategies: — Top-K-of-N, Unadjusted Langevin Algorithm (ULA), Metropolis-Adjusted Langevin
Algorithm (MALA), and our proposed -Sampler.
For all applications, -Sampler demonstrates the highest compliance with the given conditions. Additional qualitative results are provided in the main paper.
Each example visualizes the input layout with color-coded phrases and their corresponding bounding boxes for clarity. -Sampler consistently respects both the spatial constraints and object presence specified in the layout.

For each image, we overlay the predicted object centroids from a counting model for easier comparison. Additionally, we display the predicted count below each image, along with the absolute difference from the target quantity in the format (). -Sampler consistently consistently produces the most accurate results in the quantity-aware image generation task, successfully matching the specified object counts more closely than competing methods.
For each prompt (e.g., “Horse”, “Bird”), we show the predicted aesthetic score [4] below each image. While all methods generate visually plausible outputs, -Sampler consistently produces images with higher aesthetic appeal, as reflected in both qualitative impressions and the predicted aesthetic scores.
[1] Jiwen Yu et al. FreeDoM: Training-Free Energy-Guided Conditional Diffusion Model, ICCV 2023.
[2] Luhuan Wu et al. Practical and Asymptotically Exact Conditional Sampling in Diffusion Models, NeurIPS 2023.
[3] Sunwoo Kim et al. Test-time Alignment of Diffusion Models without Reward Over-optimization, ICLR 2025.
[4] Christoph Schuhmann. Laion aesthetic predictor
If you find our work helpful, please cite our paper.
@article{yoon2025psi,
title={Psi-Sampler: Initial Particle Sampling for SMC-Based Inference-Time Reward Alignment in Score Models},
author={Yoon, Taehoon and Min, Yunhong and Yeo, Kyeongmin and Sung, Minhyuk},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2506.01320},
year={2025}
}